Options Trading Explained: How Calls, Puts, and Risk Really Work
Most beginners search for options trading because nobody breaks it down calmly. It’s either too technical or too promotional. Options trading is one of the most misunderstood things in the stock market. This is one of the more advanced approaches under types of trading, involving contracts rather than direct ownership of shares.
Some people think it’s easy money. Others think it’s pure gambling. Both are wrong.
So let’s do this the right way.
Slow. Clear. Practical.
What Is Options Trading? (Options Trading Explained Simply)
At its core, options trading is about buying or selling a right, not an obligation.
That’s the key difference most people miss.
In options trading:
-
You don’t buy shares directly
-
You trade contracts based on shares
-
You’re dealing with probabilities, not ownership
I find it interesting how people jump into options without first understanding this basic idea.
If I had to explain options trading in one line, it would be:
Options trading is the buying and selling of contracts that give you the right to buy or sell a stock at a specific price within a fixed time.
That’s it. Everything else builds on this.
Where Options Trading Fits in Types of Trading
Options trading sits under the broader category of types of trading, but it behaves very differently from equity-based trading styles.
Unlike:
-
intraday trading
-
swing trading
-
delivery trading
Options trading:
-
Uses leverage
-
Has expiry dates
-
Can lose value even if price doesn’t move
From my experience, this is where many traders get surprised.
How Options Trading Works (Step-by-Step)
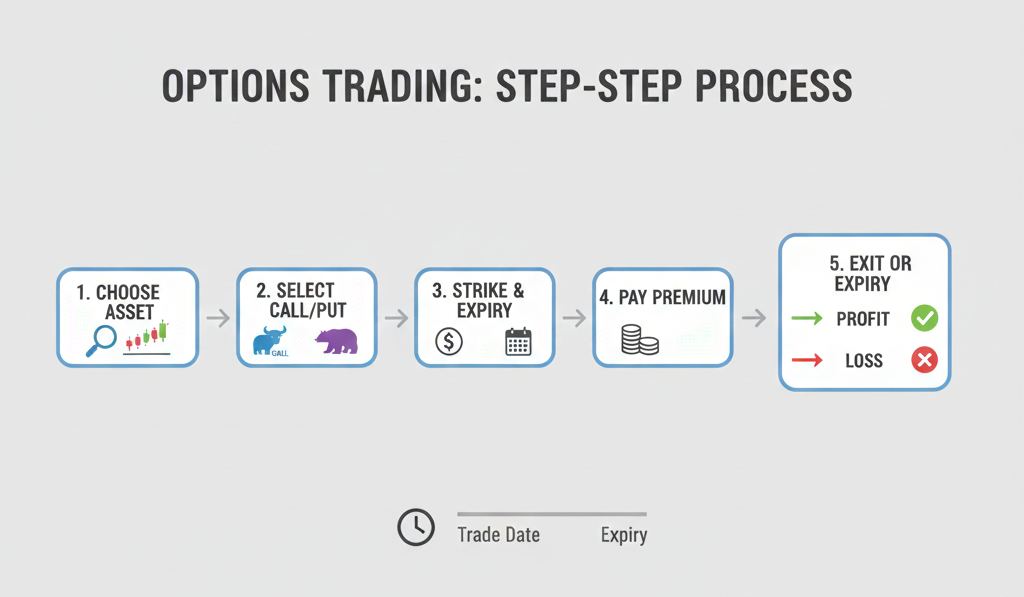
Let’s walk through the actual flow.
Step 1: Choose the underlying asset
Options are based on:
-
Stocks
-
Indices
You’re not trading the asset itself. You’re trading a contract linked to it.
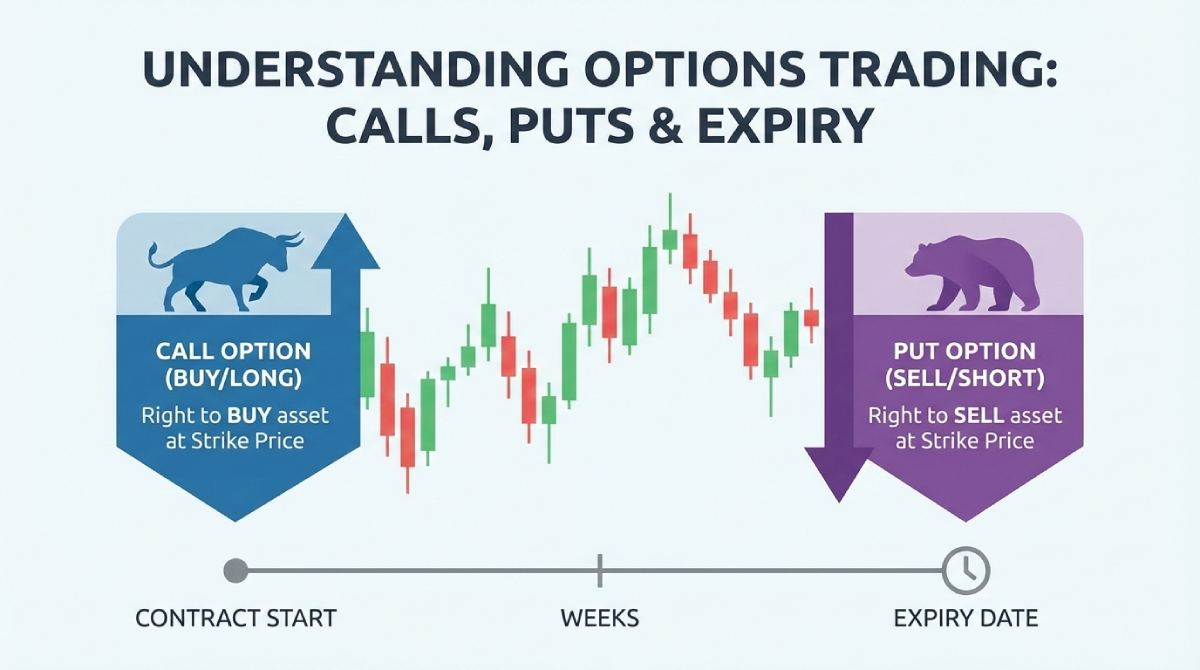
Step 2: Select Call or Put option
-
Call option → you expect price to go up
-
Put option → you expect price to go down
Simple logic. Execution is where complexity starts.
Step 3: Choose strike price and expiry
This is critical.
You must decide:
-
At what price you want the right
-
By which date
From my experience, beginners underestimate how important expiry selection is.
Step 4: Pay premium
The premium is:
-
The price of the option
-
The maximum loss for buyers
This is one of the few comforting things in options trading—loss is predefined for buyers.
Step 5: Exit or expiry
You can:
-
Sell before expiry
-
Hold till expiry
-
Let it expire worthless
That’s the basic lifecycle of options trading explained practically.
Call Options vs Put Options
This confusion never goes away unless explained properly.
Call Options
-
Used when bullish
-
Gain value if price rises
-
Lose value if price stagnates or falls
Put Options
-
Used when bearish
-
Gain value if price falls
-
Lose value if price stagnates or rises
I’ve noticed beginners often get the direction right but still lose money. That’s because options are affected by more than just direction.
Options Trading vs Intraday Trading
This comparison matters.
Intraday trading
-
Direct price movement
-
No expiry
-
Lower complexity
Options trading
-
Direction + time + volatility
-
Expiry pressure
-
Higher complexity
From my experience, people coming from intraday trading underestimate options risk initially.
Options Trading vs Delivery Trading
This is a mindset difference.
-
Ownership-based
-
Long-term focused
-
Less leverage
Options trading
-
Contract-based
-
Short-term focused
-
High leverage
I find it interesting how delivery traders value patience, while options traders are forced to respect timing.
Risks in Options Trading (Don’t Skip This)
Let’s be blunt.
Options trading is high-risk if misunderstood.
Major risks include:
-
Time decay
-
Wrong strike selection
-
Over-leverage
-
Emotional overtrading
From my experience, most losses in options trading come from overconfidence, not lack of knowledge.
If you’re learning options trading explained seriously, risk management must come before strategy.
Capital Requirements for Options Trading
You don’t need huge capital to start.
But that doesn’t mean you should trade aggressively.
Options allow:
-
Small capital entry
-
But large percentage losses
I’ve seen small accounts grow fast—and blow up faster.
Common Mistakes Beginners Make in Options Trading
These patterns repeat endlessly:
-
Trading without understanding Greeks
-
Holding options till expiry blindly
-
Overtrading daily
-
Treating options like lottery tickets
I find it interesting how people blame the instrument when the real issue is discipline.
Is Options Trading Good for Beginners?
Honest answer: Only after basics are clear.
Beginners should:
-
First understand equity and delivery trading
-
Learn market behavior
-
Then approach options slowly
From my experience, options trading rewards preparation, not curiosity.
Personal Observations (Hard Truth)
From my experience:
-
Options trading exposes emotional weakness fast
-
Small mistakes get amplified
-
Discipline matters more than strategy
I’ve noticed traders who survive options trading usually have strong foundations in other trading styles.
FAQs: Options Trading Explained
1. Is options trading gambling?
No, but without knowledge it becomes gambling.
2. Can beginners do options trading?
Yes, but only after learning basics and risk management.
3. Is options trading safer than intraday?
No. It’s more complex and riskier if misused.
4. What is the biggest risk in options trading?
Time decay and over-leverage.
5. Do options always expire worthless?
No, but many do if poorly chosen.
6. Can options trading give fixed income?
No. There are no guarantees.
7. Is options trading suitable for long-term investing?
No. It’s primarily a short-term trading instrument.
8. How long does it take to understand options?
Several months with consistent learning and practice.
Final Thoughts
If you were searching for options trading explained without hype, here’s the truth:
-
It’s powerful
-
It’s risky
-
It demands respect
Options trading is not evil.
But it punishes shortcuts.
Learn slowly. Trade smaller.
That’s how options trading survives.