Types of Trading: A Complete Guide to Choosing the Right Trading Style
Most beginners think trading starts with charts.
It doesn’t.
It starts with choosing the right type of trading. Before understanding the various trading styles, it is important to first understand what trading is and how it works at a basic level.
I find it interesting how people jump into intraday or options trading without ever asking a basic question:
Does this trading style even match my time, mindset, and risk tolerance?
That single mistake explains why most traders struggle early.
This pillar article explains the major types of trading, why each exists, how it works, and who it’s actually meant for. Think of this as a decision guide, not just definitions.
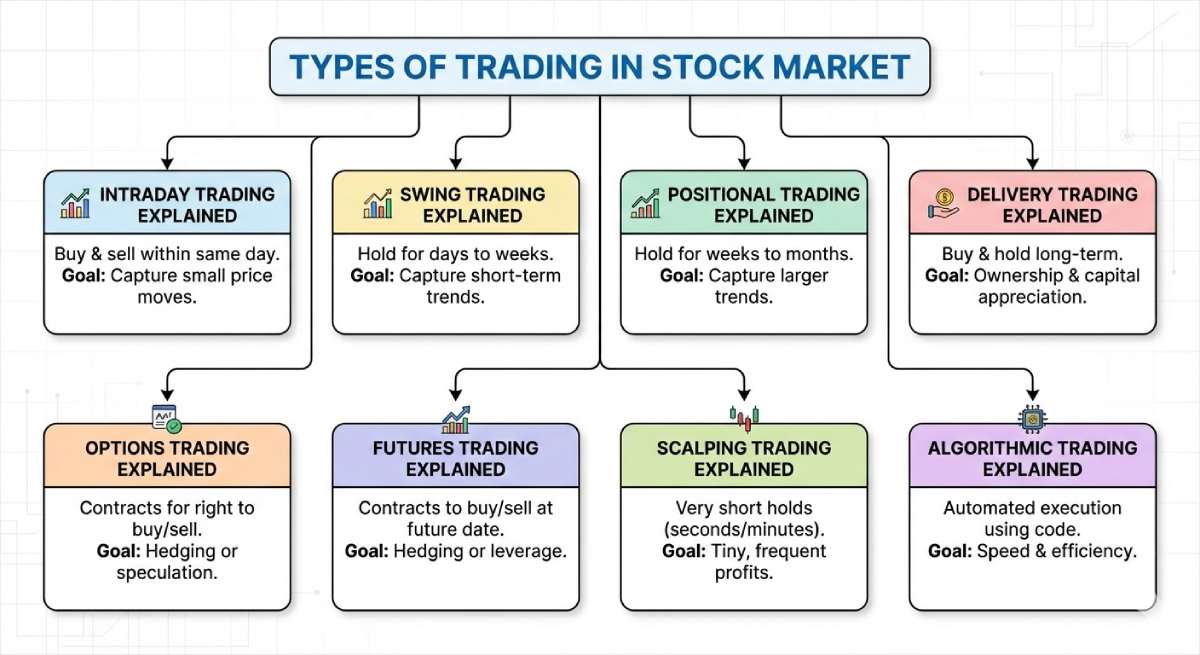
Types of Trading in Stock Market
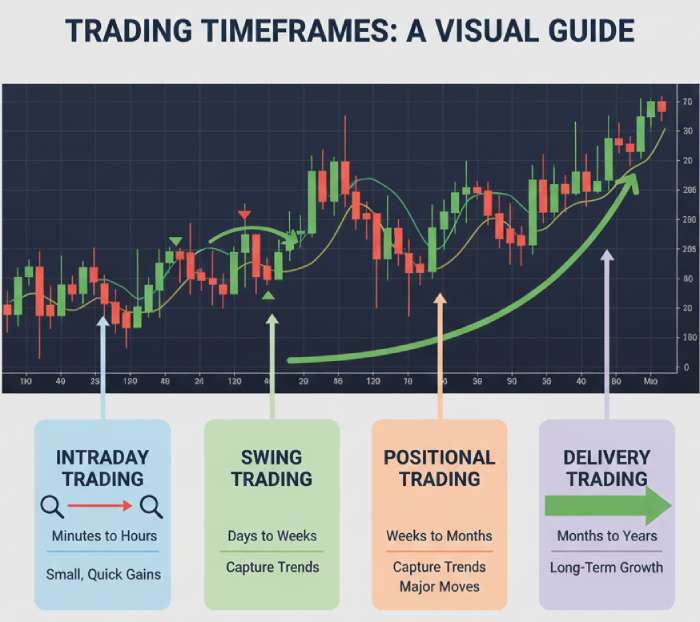
The stock market allows multiple trading styles because prices move at different speeds:
-
Minute to minute
-
Day to day
-
Week to week
-
Month to month
Each movement created a different type of trading.
There is no universal “best” trading style.
There is only the right trading style for you.
Let’s break them down properly.
Intraday Trading Explained
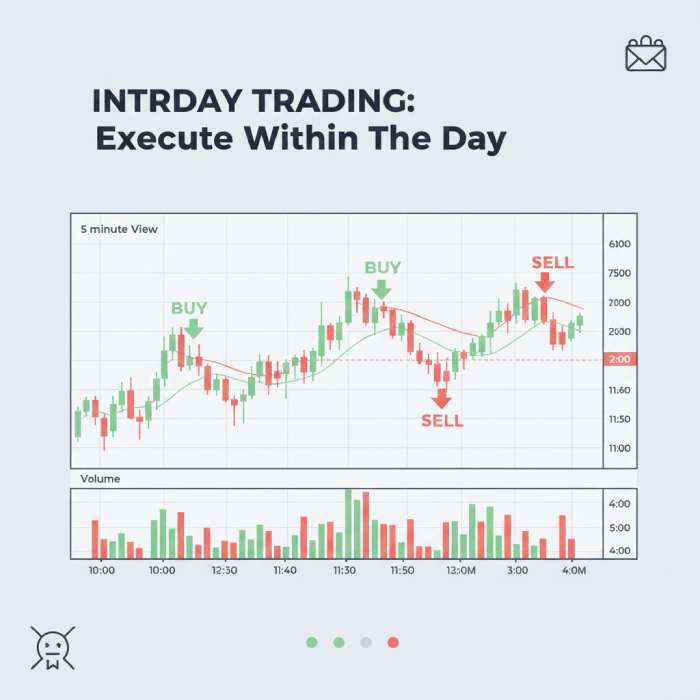
Intraday trading means buying and selling a stock within the same trading day. All positions are closed before the market ends.
Why Intraday Trading Exists
Stock prices move constantly during market hours due to news, institutional orders, and sentiment. Intraday trading tries to capture small price movements from these fluctuations. To understand how same-day buying and selling works in practice, read this detailed guide on intraday trading explained.
Why People Are Attracted to Intraday Trading
-
Quick results
-
No overnight risk
-
Appears to need less capital
The Reality
From my experience, intraday trading is emotionally demanding. Decisions are fast. Mistakes are punished immediately. Overtrading is common.
Who Should Do Intraday Trading
-
Full-time traders
-
Highly disciplined individuals
-
Traders with strict risk management
Who Should Avoid It
-
Beginners
-
Part-time traders
-
Emotion-driven decision-makers
Swing Trading Explained
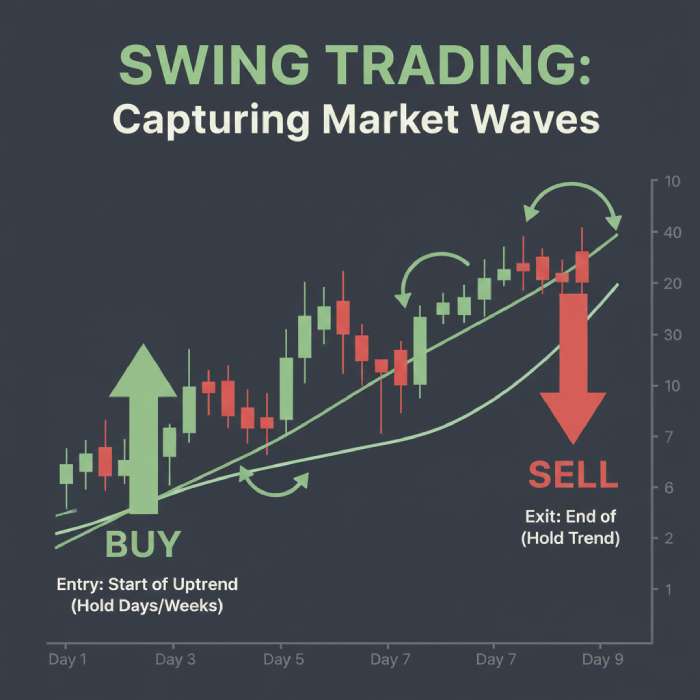
Swing trading involves holding trades for a few days to a few weeks, aiming to capture medium-term price moves.
Why Swing Trading Exists
Markets move in waves, not straight lines. Swing trading focuses on capturing these price swings rather than small intraday noise.
Why Swing Trading Is Better for Most Beginners
-
Less screen time
-
More time to plan
-
Better risk-to-reward
Personally, I find swing trading to be the most balanced approach. It teaches patience and structure without constant stress.
Who Should Do Swing Trading
-
Beginners
-
Working professionals
-
Calm, analytical traders
Positional Trading Explained
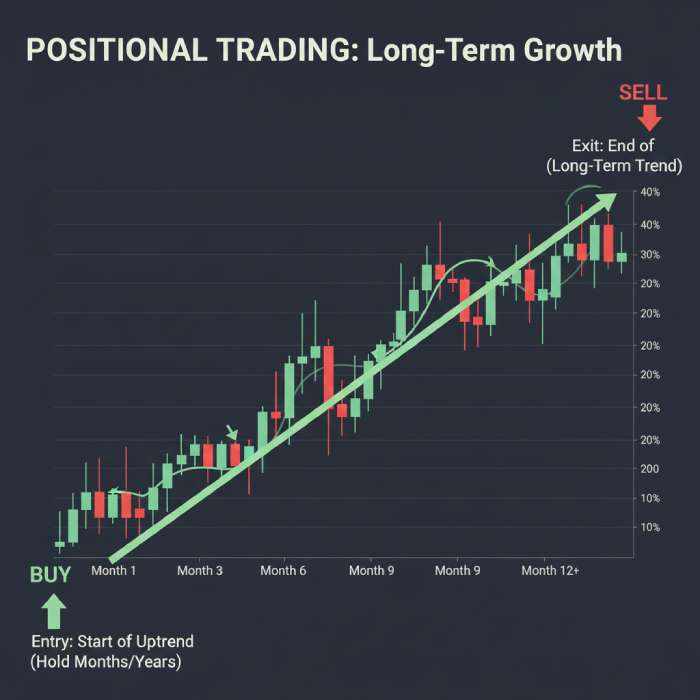
Positional trading means holding trades for months, sometimes longer, based on long-term trends.
Why Positional Trading Exists
Large trends don’t end in days. Positional traders aim to stay aligned with major price movements while ignoring short-term volatility.
How It Differs from Investing
Investing focuses on business fundamentals.
Positional trading focuses on price trend direction.
Who Should Do Positional Trading
-
Patient traders
-
Long-term thinkers
-
People who dislike daily market noise
This style feels boring to many beginners. Ironically, boredom often signals lower emotional risk.
Delivery Trading Explained
Delivery trading means buying shares and taking delivery into your demat account.
Why Delivery Trading Exists
It allows participation in price movement without leverage or forced exits.
Why Beginners Prefer Delivery Trading
-
No margin pressure
-
No compulsory square-off
-
Lower emotional stress
Limitations
Capital can remain blocked for long periods. Returns are slower compared to leveraged trading.
Who Should Do Delivery Trading
-
Absolute beginners
-
Conservative traders
-
Learners focusing on fundamentals of price movement
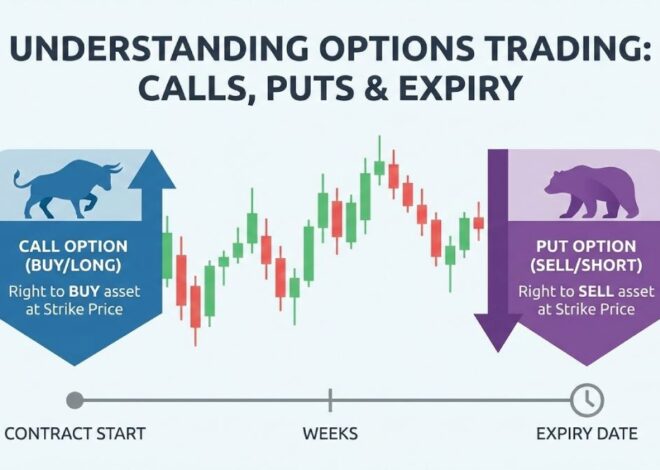
Options Trading Explained

Options trading involves trading contracts, not actual shares.
Why Options Trading Exists
Options were created to:
-
Hedge risk
-
Define maximum loss
-
Use capital efficiently
Why Many Beginners Lose Money
Options prices depend on time and volatility, not just direction. Even correct price prediction can result in loss.
From what I’ve seen, beginners often treat options as lottery tickets. That approach rarely ends well.
Who Should Do Options Trading
-
Experienced traders
-
People who understand risk deeply
-
Traders with strong discipline
Options are not dangerous by nature. Lack of knowledge is.
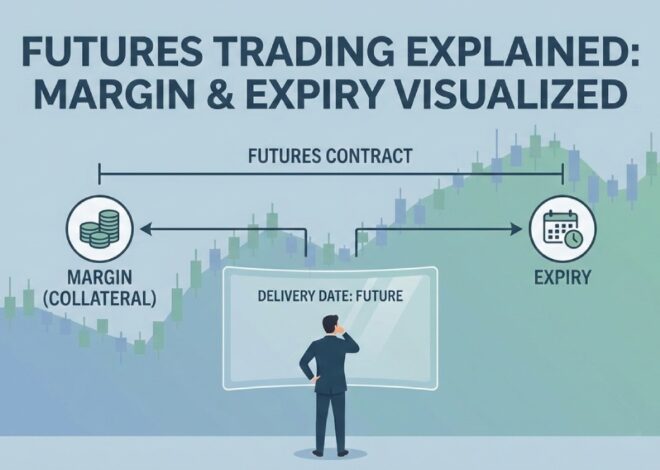
Futures Trading Explained
Futures trading involves agreements to buy or sell an asset at a fixed future date.
Why Futures Trading Exists
It allows traders to participate in strong trends using leverage and to hedge large positions.
Risk Factor
Losses can increase rapidly if positions are unmanaged.
Who Should Do Futures Trading
-
Traders with sufficient capital
-
Strong risk management skills
-
Emotional control
Futures reward discipline and punish carelessness.
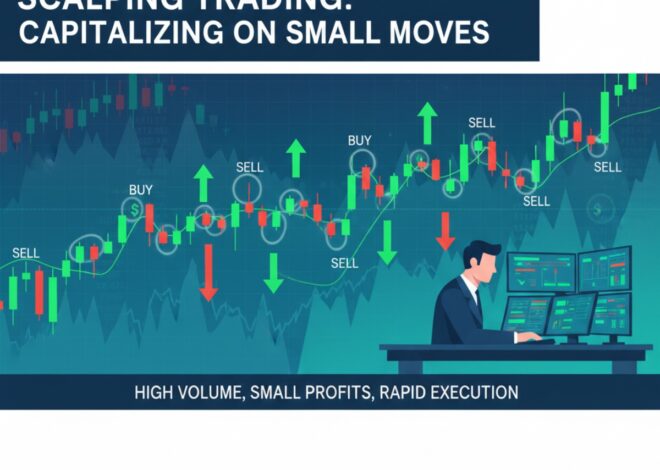
Scalping Trading Explained
Scalping trading focuses on very small price movements, executed many times in a single session.
Why Scalping Exists
Markets provide micro-movements continuously, which skilled traders try to exploit.
Why Scalping Is Difficult
-
Requires extremely fast execution
-
High mental fatigue
-
One mistake can erase many gains
Who Should Do Scalping Trading
-
Highly experienced traders
-
Traders with strong execution skills
Who Should Avoid It
-
Beginners
-
Emotionally reactive traders
Algorithmic Trading Explained
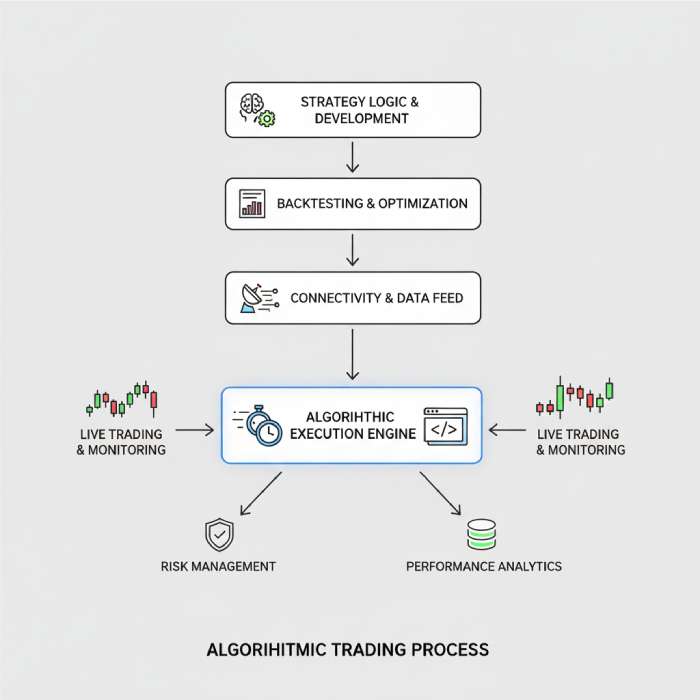
Algorithmic trading uses computer programs to execute trades automatically based on predefined rules.
Why Algorithmic Trading Exists
-
Removes emotional bias
-
Improves execution speed
-
Maintains consistency
Common Misconception
Algorithmic trading is not “set and forget.” Strategies need constant testing and adjustment as markets change.
Who Should Do Algorithmic Trading
-
Tech-savvy traders
-
Logical thinkers
-
People comfortable with data and testing
Algorithms reduce emotion, not risk.
How to Choose the Right Type of Trading
Choosing the right trading style becomes much easier once you understand the trading basics and how the market works overall. Here’s a practical framework:
-
Beginner + low stress → Delivery or Swing trading
-
Working professional → Swing or Positional trading
-
Full-time trader → Intraday or Futures trading
-
Technical background → Algorithmic trading
Your trading style should fit your lifestyle, not your ego.
Final Takeaway
Types of trading are tools.
Tools don’t make money.
Discipline does.
Old rules still win:
-
Simple styles last longer
-
Slow learning beats fast losses
-
Mastery beats experimentation
Pick one type of trading.
Learn it deeply.
Respect risk.
No matter which style you choose, long-term success depends on mastering the fundamentals of trading and managing risk consistently.
That’s how traders survive — and grow.